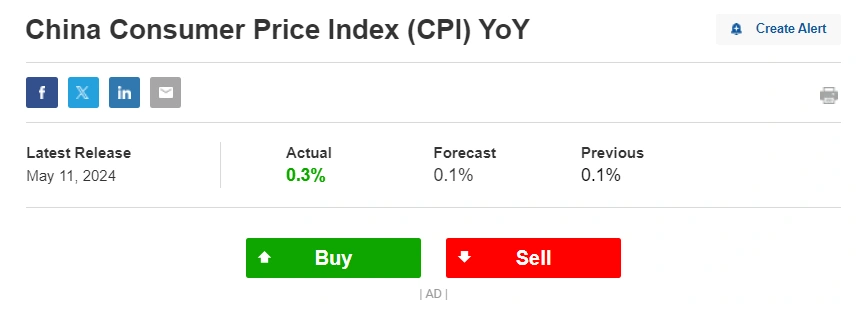
China CPI: Inflation is a critical economic indicator that reflects changes in price levels over time. In China, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) serves as the primary measure of inflation. Let’s explore the key aspects of China’s CPI and inflation trends.
Understanding China’s CPI and inflation trends is crucial for policymakers, investors, businesses, and consumers alike as they navigate the complexities of the Chinese economy.
Read More: Sanofi Q4 2024: A Powerful Year of Corporate Empowerment
Table of Contents
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) serves as a vital economic indicator, tracking the average price changes of a representative basket of goods and services consumed by urban and rural residents.
Asian stocks drift higher as CPI test approaches; China dips on US tariffs https://t.co/NlqJcg30yQ Follow for more #Breaking #Stockmarket #StockMarketNews pic.twitter.com/VMGaKhP9pg
— ProfitTradingUSA (@ProfitTradingUS) May 15, 2024
This comprehensive index offers valuable insights into the fluctuations in the cost of living experienced by the general population.
Understanding the CPI is crucial for policymakers, economists, businesses, and individuals alike, as it helps assess inflationary pressures, adjust economic policies, and make informed financial decisions.
Click here to delve deeper into the significance of the CPI and its implications for various stakeholders.
What is China CPI 2024?
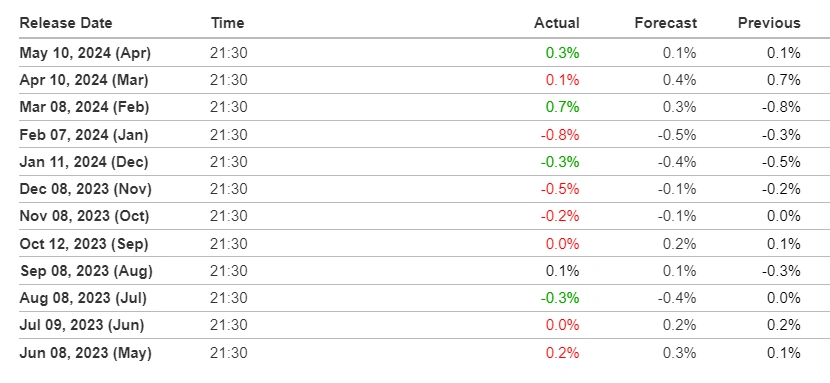
China’s inflation rate in 2024 has been on the rise, but it’s still quite low compared to recent years. Here’s a breakdown:
| Overall Trend | After a period of deflation in 2023, China’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) has been ticking upwards for the past few months. |
| Current Rate | As of April 2024, the inflation rate sits around 0.3% year-over-year. This means prices are slightly higher than they were in April 2023. |
| Predictions | Analysts forecast a full-year average inflation rate of around 0.5% for 2024. This low number reflects weak domestic demand, but it could rise slightly due to factors like |
| 1. Food Prices | A potential increase in food prices could push inflation up a bit. |
| 2. Stable Core Inflation: | The cost of non-food items is expected to remain relatively steady. |
| 3. Government Stimulus | The Chinese government might implement policies to boost spending, which could lead to some price increases. |
Impact: Low inflation in China has both positive and negative consequences:
- Positive: It helps keep prices stable for consumers and businesses.
- Negative: It can also indicate a sluggish economy with weak consumer demand.
Looking Ahead: Whether China can achieve its economic growth target of 5% in 2024 depends heavily on how inflation and consumer spending evolve in the coming months.
Historical Trends of China CPI
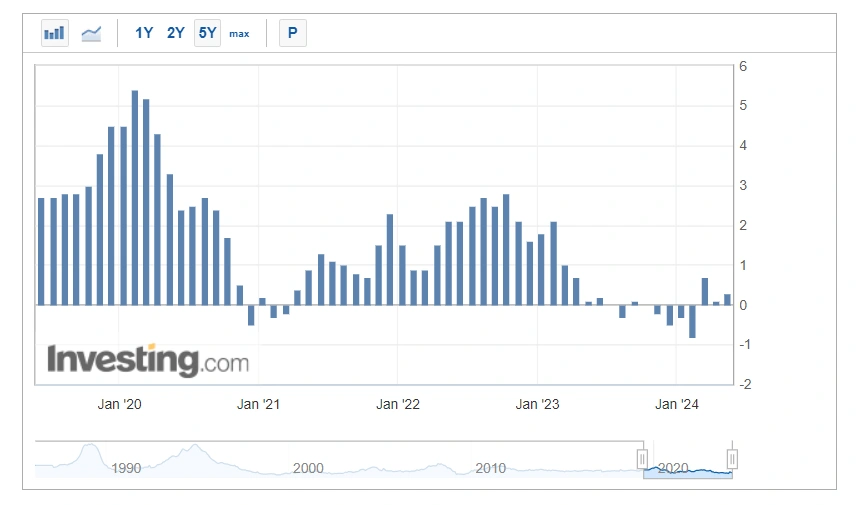
- Over the past two decades, China’s inflation rate has remained relatively low and stable, averaging around 2.4% annually.
- Notably, China’s inflation figures may not fully capture the rising cost of living experienced by residents in fast-growing cities and urban areas due to varying accounting methods.
Recent Developments in China CPI
| 2021 | Inflation picked up, reaching 2.8% in September 2022. Rising costs for fuels and raw materials were key drivers. |
| 2022 | Inflation eased but remained lower than in other major economies. Food prices also contributed to the overall increase. |
| 2023 | Due to the sluggish economic recovery post-COVID-19, consumer prices showed deflationary tendencies. |
| 2024 | Inflation is expected to remain low due to limited demand. |
Factors Impacting China’s CPI
- Food Prices: China’s large population and changing dietary habits significantly influence food prices. Fluctuations in grain, meat, and vegetable prices directly affect the China CPI.
- Housing Costs: Rapid urbanisation and property market dynamics impact housing costs. Rent, utilities, and property prices contribute to inflation.
- Energy and Fuel: Global energy prices affect China CPI. Rising oil prices impact transportation costs and household energy bills.
- Monetary Policy: The People’s Bank of China adjusts interest rates and money supply to control inflation. Tightening or easing monetary policy influences consumer spending.
Regional Disparities
China’s vastness leads to regional disparities in inflation. Coastal cities experience higher living costs, while rural areas have lower inflation rates.
Inflation vs. Deflation
Inflation erodes purchasing power, but moderate inflation is essential for economic growth.
Deflation (falling prices) can lead to reduced spending and economic stagnation.
International Comparisons
China CPI inflation rate is lower than that of many developed economies.
Comparing CPIs globally helps assess relative cost of living and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, China CPI story in 2024 is one of slow and steady growth. While prices are finally rising after a period of deflation, they’re still moving at a very slow pace. This low inflation keeps things predictable for consumers, but it also reflects a lack of strong economic activity. Whether China can hit its ambitious growth target hinges on how inflation and consumer spending pick up in the remaining months of the year.
Disclaimer: All information provided in this summary is sourced from various internet and news sources and is presented for informational purposes only. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any information presented herein. Readers are advised to independently verify any information before making decisions based on it.
FAQs
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The CPI measures changes in the average prices of a basket of goods and services consumed by households. It reflects inflation or deflation trends and helps assess the cost of living.
How did China’s CPI change in March 2024?
In March 2024, China CPI increased by 0.1 percent year-on-year. Urban areas saw flat prices, while rural areas experienced a 0.1 percent increase. Food prices decreased by 2.7 percent, while non-food prices increased by 0.7 percent.
What were the specific price changes for different categories in March 2024?
Food, tobacco, and liquor prices decreased by 1.4 percent year-on-year, affecting the CPI. Notably, egg prices dropped by 8.9 percent, fresh fruit prices by 8.5 percent, and meat prices by 4.3 percent. Aquatic products increased by 1.2 percent, and grain prices rose by 0.5 percent.
How did the CPI change month-on-month in March 2024?
In March, the national CPI decreased by 1.0 percent compared to February. Urban areas saw a 1.0 percent decrease, while rural areas decreased by 0.7 percent. Food prices dropped by 3.2 percent, and non-food prices decreased by 0.5 percent.
What about other categories?
Miscellaneous goods and services, education, culture, and recreation prices increased year-on-year, while transportation and telecommunication prices decreased. Month-on-month, food prices declined by 2.2 percent, affecting the CPI, especially fresh vegetables (down 11.0 percent) and meat (down 3.9 percent).
What’s the inflation outlook for China CPI in 2024?
Economists expect China CPI to average 2.2 percent in 2024, up from 2 percent in 2022. The index could rise to 107.29 points based on econometric models.
Remember that CPI data can impact economic policies, investment decisions, and everyday life. If you have more questions, feel free to ask!